From Blockchain to Ecosystem
EDIT 05/08/2020: Vitalik Buterin came up with the idea for AMMs in late 2016. I didn’t know about his idea at the time I was writing AIP22 and this article. I would like to acknowledge his genius and recommend readers to read his blog post as well. – END EDIT –
The internet revolution started with a small group of scientists who figured out how to connect computers separated by vast distances. The simple act of connecting computers into a single network has made such a great impact on society that no facet of our life today can work without it. In this post I will try to convince you that the same revolution is about to happen in the world of cryptocurrencies and that Ark is poised to lead it. I will also try to outline one way in which we could achieve this and connect multiple blockchains into a single internet of blockchains, and how it’s consequences will cause disruption on the same scale as the internet did when it finally matured.
Ideological Foundations
In October of 2008 a pseudonymous entity going by the name of Satoshi Nakamoto published the bitcoin whitepaper that heralded the era of decentralized cryptocurrencies. When Satoshi released an implementation of the bitcoin protocol in 2009 he made it very clear that his motivations for creating bitcoin were ideological. In the very first block that he mined on the bitcoin network he encoded the words “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks”. It made obvious the fact that he wanted bitcoin to be a rebellion against the tyranny of fractional reserve banking. This ideology resounded with many people who went on to become early adopters and pioneers of cryptocurrencies.
Bitcoin was created right in the wake of the global economic collapse of 2008 but today many people might be asking the question: Why is the central banking system bad and how does cryptocurrency intend to solve that? This can be answered by observing the implications of proper decentralization in networks. Decentralized networks by definition have no central authority that can single handedly dictate decisions on the network. These networks work by groups of people connecting with each other on an individual peer to peer basis and contributing to the network for collective and selfish benefit. The incentives in such a network are designed to reward people for providing services to the network in the form of newly minted tokens. As a result a decentralized network does not allow anyone to force their will on others and become tyrants. Another implication of decentralization is that since the transactions on the network are peer to peer there are no intermediaries who extract value out of the network and inhibit economic growth. In conventional systems we notice that since the central governing body has limited resources and manpower, they often become the bottleneck for innovators that want to contribute, and hinder growth of the network as a whole. However because there is no central entity dictating the future of the network in decentralized networks, innovation can happen at all nodes instead of the center and there is no bottleneck. Lastly the capacity of the network to provide a certain service grows as more and more people join the network and as a result there are more people joining the network and becoming service providers on the network. This makes it so that such decentralized systems grow at an exponential rate until they fill their niche. In the case of cryptocurrencies that niche is the entire GDP of the world since any asset can be represented and traded in the form of cryptocurrencies instead of fiat or invoices/pay orders.
The points mentioned above are in stark contrast to the conventional financial system where central entities make decisions and are often found misusing their position of power. Additionally the fact that central banking has failed to deliver basic banking services to roughly 1.7 billion adults across the world (31% of all adults) despite existing in traditional form for centuries and with digital technologies for decades is a great example of how it is failing to grow to fulfill global demand and enable value creation and prosperity in developing regions. Therefore I would argue that the global financial industry is ripe for massive disruption at the hands of cryptocurrencies and we will see this play out in the next 5 years or so.
Introduction to ARK
Ark is a cryptocurrency project started by some of the aforementioned early adopters of cryptocurrencies. It aims to solve the drawbacks that the bitcoin protocol has. Some of the issues plaguing bitcoin today are high energy footprint, lack of protocol for social concensus, and scaling. Ark uses a modified form of the concensus mechanism introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto, known as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) which allows for the creation of very efficient networks that are governed democratically through voting on the network. We may discuss in detail the concensus and social governance mechanism of Ark in a future post however I would like to focus on Ark’s scaling strategy for now because it holds the most significance for the future of cryptocurrencies.
Ark’s Scaling Strategy
While Satoshi’s invention of the blockchain was a major breakthrough the followup development of Bitcoin has ended up at a dead end in which the network has stalled and can’t scale further to accomodate a higher transaction throughput due to the failure of social governance in the absence of a proper social concensus system. This was most evident in December 2017 when the cost of a single transaction went to a record high of 50$ because the block limit of 1MB was reached and there was no room to place any more transactions in the blocks. The debate around bitcoin’s scaling problem has seen solutions being proposed such as raising the block size so that more transactions can be included, and implementing layer 2 solutions that take transactional volume off chain in order to reduce workload. Even in the presence of such scaling solutions there is still a misalignment of incentives as the network intends to have several thousand miners, to ensure that no single entity or group can control the network, but increasing the block size past a certain size means that smaller miners are pushed out of the system because their systems can’t keep up with the rest. As a result bitcoin and other proof of work (PoW) systems have a maximum transactional capacity past which the network starts deteriorating and forks itself into oblivion as new blocks can’t be propagated quickly enough.
There are only two real solutions to the problem discussed above.
1) Distribute the network’s workload onto multiple blockchains instead of one single blockchain. This approach is called multichain scaling or sharding.
2) Allow smaller contributors a voice in the network’s decisions by delegating votes to other contributors and pooling together. This allows a mechanism to democratically elect best contributors to the ecosystem and also allows to immediately punish bad actors since the votes can be taken away immediately.
As you may have guessed already Ark adopts both of these solutions. Some of you may argue that proof of stake (PoS) approaches like those being pursued by Ethereum and Cardano also offer better scaling solutions than traditional PoW without depending on delegation. To that I would like to point out the existence of delegation in those approaches the form of Rocket pool in Ethereum and proxy voting in Cardano’s Ouroboros Praos mechanism. I would also argue that such mechanisms don’t provide the necessary tools that allow small contributors in the network to have a voice in matters i.e because staked amounts are locked for a significant amount of time in both of these protocols smaller contributors have no way to socially punish bad behavior by the pool/proxy in time for it to make a difference. Therefore I would like to bring to attention the fact that not only are PoS systems also becoming more like Ark, in what can be called a convergant evolution to an optimum design, but also that PoS systems lack the tools that safeguard the smaller members of the network.
The goal of Ark’s main chain is to serve as an on/off ramp to the Ark Ecosystem. The ecosystem involves multiple specialized side-chains (often called bridge-chains) that bring unique functionality to the table. For example one chain in the ecosystem may bring storage as a service, while another may provide personal identity and user authentication service to the entire ecosystem. This ability for different chains in the ecosystem to communicate with each other is enabled through a small data field contained by all transactions on the ecosystem. This data field is known as a smartbridge due to it’s ability to bridge different chains. The data contained in the smartbridge is public and any node in the network can read it. As a result any individual can connect two different chains together by setting up specialized nodes that read data from one chain and transmit appropriate data onto another chain. In addition to the ability to transfer data across different chains in the ecosystem the Ark protocol will soon have the ability to transmit value across chains in the form of atomic swaps. Atomic swaps are paired transactions that either succeed together or fail together, there’s no way to have one transaction succeed and the other fail. This feature of atomic swaps is very useful to allow cross chain transactions without intermediaries or escrow. A proof of concept that uses centralized nodes to transmit value across chains called ACES has already been implemented and tested in the Ark Ecosystem, we will discuss it in more detail in a later section.
This was a brief introduction to what the Ark Ecosystem is. In the rest of the article we will discuss what the Ark Ecosystem can be. Before I continue I have to clarify that I am not a part of the Ark.io team. Everything mentioned from this point onwards is my vision of ark as a community member and contributor, and it may differ from the Ark team’s vision. With that being said I would like to add that I am contributing to the Ark Ecosystem, as well as becoming a delegate, in a bid to make my vision a reality by raising social awareness and lobbying for the technical solutions I present such as the one below.
Markets
By this point I hope I have convinced you that Ark is a legitimate contender to become the dominant crypto-economic ecosystem of the world. It should be clear now what the Ark Ecosystem wants to achieve. However one may still ask the question of how this will all be achieved. After all, other cryptocurrencies have existed for a longer time and they have had the ability to perform atomic swaps as well. What makes Ark better suited to achieve the stated goal than any of the others? In order to explain this we need to understand why the other cryptocurrencies failed, and that starts with understanding market fundamentals.
Markets are a place for people to buy or sell assets and determine a price value for an asset. The price of any asset is determined by the balance of supply and demand for that asset in the market. Traditional markets were physical places where people would go and haggle with each other for prices. Modern markets substitute the digital communication medium instead of meeting at a physical location but the process of bidding and buying to haggle is the same as before. This process is often explained in conventional economics studies in very complicated terms however since my goal is to reach a broader audience I will attempt to present a simple analogy that I believe gets the point across.
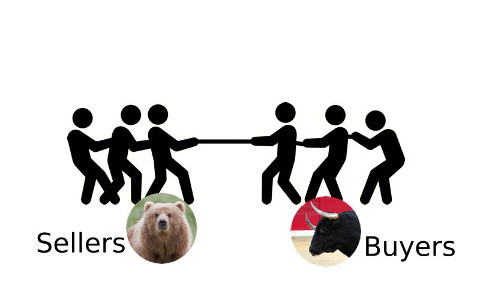
The act of bidding and accepting bids to determine a price for an asset can be seen as a tug of war contest between the buyer and the seller since the buyer is incentivized to bid the lowest possible price while the seller is inclined to take the highest possible price. One assumption that we are making in this process is that both the buyer and seller are inclined to make the trade and therefore some price will be determined for the asset at all times. If there are more sellers than buyers for a particular asset in the market then the price of the asset decreases until a balance between sellers and buyers is reached.
1 | <script src="https://d3js.org/d3.v5.min.js"></script> |
Another thing about markets that is of interest to us is that the price of an asset grows exponentially over time and finally slows down as the market adoption reaches final peak. This is because demand for assets increases through word of mouth and the more people that know about some asset the faster others will learn about it and participate in trading it. The available amount of the asset that can be traded on the market is called liquidity. Assets with low liquidity are volatile because even small orders can change the price significantly whereas assets with high liquidity are less volatile since it takes large orders to move the price by the same amount.
Since cryptocurrencies are relatively new and not yet widely adopted they suffer from a lack of liquidity as compared to traditional markets. This means that cryptocurrencies are more volatile and the price changes are more severe. Typically for any new industry the government steps in and provides liquidity to the market by providing incentives for trading and using the asset. This is done in order to increase further adoption of the particular asset in question since consumers and the general public don’t like to participate in volatile assets. However, due to the ideological background of cryptocurrencies and the fact that they threaten the government’s control over money, expecting such a step to be taken by a government is unlikely. Which essentially leaves cryptocurrencies at the mercy of consumer adoption and creates a chicken and egg problem i.e Cryptocurrencies can’t become stable assets until adoption increases and adoption won’t increase by consumers unless cryptocurrencies become more stable. The introduction and usage of stable coins similar to Tether that are pegged to fiat currencies doesn’t address the problems addressed in the beginning of the article with the conventional banking system. In a later section we discuss an approach that provides promise to solve this problem of adoption and stability.
ACES
Ark Contract Execution Services (ACES) is a proof of concept project that delivers the ability to transmit value across chains. It uses smartbridges to detect when a transaction needs to be made and to which chain and address. One shortcoming of current implemetations of ACES is that the nodes are centralized and don’t use atomic swaps. Which means that the node operator can choose to not uphold his promise and refuse to pay out on the other chain after recieving the amount on first chain. Additionally current ACES nodes only offer a fixed price for tokens and there’s no mechanism implemented that could allow price discovery of assets. Finally the liquidity for the ACES node has to be provided by the node operator and pooling together liquidity from different participants raises concerns about custodial exchange regulations and requires pre-approval from the relevant government body for each ACES node. Although to be fair the intended purpose of ACES (as evident from it’s name) is to allow execution of contracts across different chains in order to provide cross chain services.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges
As we discussed already, due to the limitation imposed on block size by block propagation time, the only option for scaling is to distribute transactions onto multiple blockchains. The sharding approach to solve this problem uses the same token across all chains but it has issues that are still unsolved. However if we wanted to use a different token for each chain in the ecosystem as is intended in the Ark Ecosystem then these token assets have to be listed on an exchange to determine a fair price. Current mechanisms adopted by exchange platforms rely on bidding and accepting bids similar to traditional markets. These exchanges take a significant cut from each trade and also extract a hefty fee for an asset to be listed on the exchange in the first place. As a result the only projects gaining traction and adoption in the current environment are those that market their product in a ponzi-esque scheme where they get listed on exchange after exchange, which not only damages the reputation of cryptocurrencies as a whole, it also disincentivizes serious projects that are not willing to invest copious amounts of money to run the ponzi-esque marketing strategy. If price discovery with high liquidity could be provided without all these drawbacks then the crypto projects can focus on building actual products that revolutionize the world and make a difference.
Introducing Liquidity Gates
Liquidity gates are a concept introduced in AIP22 by myself (mak). The purpose of liquidity gates is to solve all of the aforementioned issues by enabling price discovery via cross chain atomic swaps without an intermediary. A liquidity gate is essentially an address controlled by the delegates running the chain. As such it requires majority of forging delegates to sign off on every transaction made to or from a liquidity gate. Since delegates in a DPoS are kept in check by their voters and acquiring delegate majority is prohibitively expensive it can be proven that this method of relying on delegates instead of exchanges is just as secure as running a DPoS blockchain.
As a concrete example let’s discuss how Bob will register a bridge-chain service provider which alice can use and how alice and bob can interact with the liquidity gate.
Registering a liquidity gate is done as follows:
1) Forging delegates on a new bridgechain convert premine address into liquidity gate. After this step only transactions with required majority signatures from forging delegates will be accepted.
2) Forging delegates on bridgechain register new chain on the Ark main chain by creating a multisignature transaction by majority of forging delegates. This transaction will contain details about the network such as the network’s short name (for instance ARK or PRSN), the initial listed price of the token, as well as the formula that will be used to decide price changes. This price should be kept small initially so that it invites early adopters.
4) After registration forging delegates will listen for and sign valid atomic swap transactions initiated by buyers or sellers.
5) Delegates will keep track of price according to the formula defined in the first step.
3) When a delegate enters or leaves the forging position then a new multisignature is generated and registered on the Ark main chain.
The process of cross chain transfers through liquidity gates will go as follows:
1) Once a liquidity gate has been registered it will contain the premined amount of bridgechain tokens.
2) Alice who owns X amount of Ark wants to buy Y amount of bridgechain tokens so she creates an atomic swap and broadcasts it on the Ark network.
(X Ark -> registered liquidity gate on ark):(Y BRG -> alice’s address on bridgechain)
3) Delegates of the bridgechain listen to the transaction on the main chain.
4) They sign and propagate it on the bridgechain.
5) Alice sees the signed transaction and is now able to decode it to find a secret which allows her to retrieve the required BRG into her account.
Since the premined amount is being used directly in a liquidity gate it provides very high liquidity for anyone who wants to buy the bridgechain token. Each cross chain transaction via the liquidity gate updates asset price according to a formula. In AIP22 I propose two different types of formulas
a) Exponential price increase (similar to current assets)
b) Logarithmic price increase (can be used as stable coins)
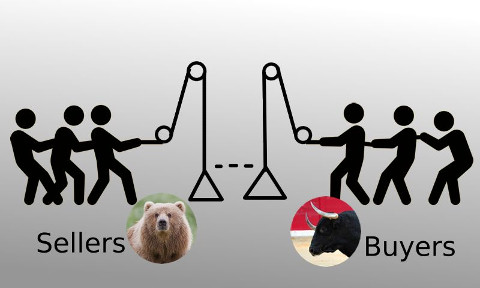
This entire operation of making a cross chain transfer can be thought of in the same metaphor of tug of war. Only this time the buyer is pulling a rope tied to a pulley system lifting a weight and the seller party is replaced by a weight that changes based on it’s height from the bottom according to required formula.
Stable Coins using Liquidity Gates
As discussed earlier we know that regular assets follow exponential price growth and therefore an exponential price change formula can be applied in a liquidity gate to mimic traditional markets and exchanges. However the more interesting thing that a liquidity gate allows is creation of stable assets using a logarithmic formula. The logarithmic formula takes advantage of the log(x) function which increases quickly when x is small and slows down the percentage rate of increase when x is large. What this enables is creating an asset that allows early investors to get high rewards similar to traditional assets but without allowing them to manipulate price significantly when adoption increases. Finally by splitting up the initial premined supply and opening up multiple liquidity gates with different cryptocurrency assets, even with fiat pegged stable coins, using the logarithmic formula the volatility of the newly created bridge coin can be reduced and it can become a stable asset much early in it’s adoption phase.
1 | <script src="https://d3js.org/d3.v5.min.js"></script> |
Conclusion
In conclusion the Ark Ecosystem is a prominent contender for the crown of being the most dominant protocol for future cryptocurrencies. Additionally Liquidity Gates are a promising approach to solve decentralized price discovery and can be implemented as part of the Ark base protocol so that the entire Ark Ecosystem can utilize them. This will ensure that the Ark Ecosystem can grow with demand and is not hampered by issues in getting bridgechain tokens getting listed on exchanges for a hefty price. Finally the logarithmic price discovery formula can be used to create stable assets unlike those that were available before and it can solve problems currently facing cryptocurrency adoption. Finally I would like to thank you for taking the time to read this article and I would like to ask you to contribute to the cryptocurrency movement and help improve the world.